Application Requirement: Students from Post-secondary education, Specific major, nationality, and education background are not required (students from undergraduate, graduate and master programs can apply).
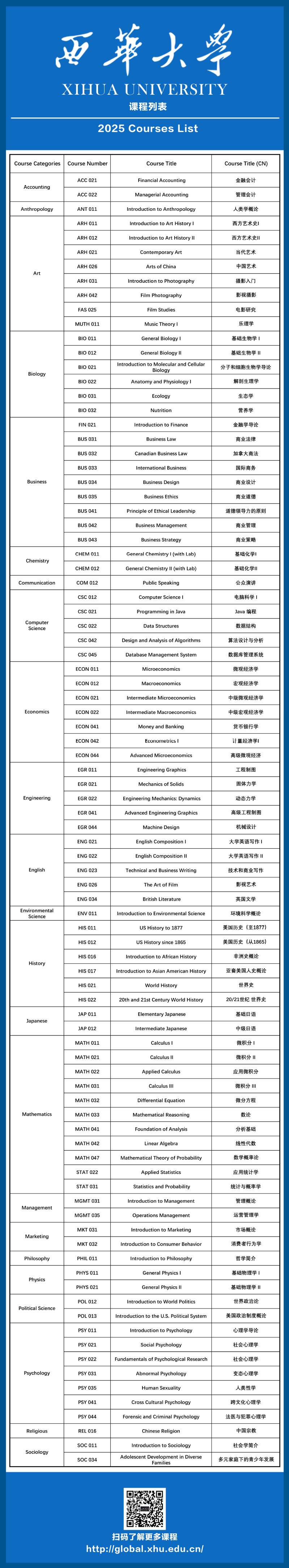
Course Description
Accounting
Course Name: Financial Accounting
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course provides students with the necessary background knowledge: 1) Understand the concepts and metrics that make up financial statements; 2) Develop the skills needed to effectively analyze financial statements; 3) Understand the choices companies make when reporting the results of their business activities. Topics include understanding operating cycles, accounts receivable, inventory, plant and equipment, intangible assets, liabilities, bonds, ownership and shareholder equity. Special topics include present value theory, calculations and applied mathematics.
Course Name: Managerial Accounting
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
Budgets, controls, responsibility, fixed costs, variable costs, mixed costs, activity-based costing, balanced scorecards, decision-making, cost-volume-profit, pricing.
Anthropology
Course Name: Introduction to Anthropology
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course introduces anthropology. In order to understand humans themselves, anthropologists have added many different methods and tools to explain how humans interact and how they function. Anthropologists have investigated our biological and evolutionary roots, and explored the development of culture in prehistoric and historical periods. They also explored the unique ability of human beings to develop culture through communication. We will discuss from several fields: cultural anthropology, archaeology, natural anthropology and linguistic anthropology. You will learn about their unique methods and how they can be applied to solve global problems in today's complex and changing world.
Art
Course Name: Introduction to Art History I
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
Ancient to Medieval History of Western European Art and Architecture is a general introduction to the history of western European art, its ancestry and its heritage. It is designed for the beginning student and assumes no previous experience in art or art history. In addition to lectures, students will be expected to participate in class discussions.
Course Name: Introduction to Art History II
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
You will study the main movements and influential artists in Western art history from the fifteenth century to the twentieth century. Looking at major developments in painting.sculpture and architecture from the Renaissance to Modern art, you will become familiar with and be able to explain a number of regional styles and individual works. This course aims to provide you with an understanding of the historical framework of certain artistic movements and why they developed in their place and time. You will gain tools to analyze and understand iconography, color, perspective, form, etc., to take beyond the classroom into the visual world around you. Although we will be categorically and chronologically studying certain movements to provide a broad foundation of understanding, the course will ultimately attempt to show the flow between these styles and movements to see how the actions and reactions between subject and object make these works of art so unique and interesting.
Course Name: Contemporary Art
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
The course focuses on American and European art produced since 1945, but will also
consider art from other cultures. Students examine artwork and its cultural context with the aim of recognizing, understanding and discussing various art forms in a broader context. The course also aims to introduce students to the subject of art history and enable them to answer fundamental questions. This course focuses on themes that run through contemporary art, including issues of identity, avant-garde art, art and artwork, institutions and challenges to them, and branding and marketing in the art world.
Course Name: Arts of China
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course explores a selection of major developments in Chinese visual and material culture from ancient times to the present day. Works in multiple media including bronzes, pottery, sculpture, calligraphy, paintings, ceramics and installations will be discussed Different POV will be made through the society, the relationship of art to politics, the religion and literature. Topics including: landscape painting, pictorial and sculptural programs of Buddhist grottoes; art collected by the imperial court; Daoist, Buddhist, and Confucian religious practices; Effects of foreign styles and ideas; and the role of Chinese artists in the contemporary world.
Course Name: Introduction to Photography
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course is to introduce students the digital photography. Students will learn
about different camera techniques, to see and design shapes in the frame.
Students will be introduced photography to both contemporary and history practice.
We will engage in traditional forms of image making while embracing new media
and digital manipulation.
Course Name: Film Photography
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
An introduction to materials, equipment, technology and design concepts used in film
photography. It is a general survey of film photography, focusing on the practice and
production of darkrooms, image composition, vocabulary, art history, and the technical
skills necessary to successfully print films and photos in darkrooms.
Course Name: Introduction to Film Studies
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This class provides an introduction to the basic tools of film analysis. We will examine how elements like mise-en-scène, cinematography, editing and sound work together to create meaning in a range of films. We will also examine how these elements are put together in different types of films narratives,documentaries and experimental cinema and how films function in society to circulate ideas and ideologies. Intro to Film Studies provides you with the skills to analyze film aesthetics, as well as the tremendously important role movies play in our culture.
Course Name: Music Theory I
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course provides an introduction to elements of music: properties of tone and rhythm, sight reading from bass and treble clefs notation of meter and rhythms construction of scales and beginning harmony, triads, and intervals ear-training, sight-singing, analysis and compositional work.
Business
Course Name: Introduction to Finance
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course provides an overview of fundamental ideas of finance, such as the time value of money, risk and return, the cost of capital, and the no-arbitrage principle. Emphasis will be placed on capital budgeting, financial asset valuation, portfolio theory, and capital asset pricing theory.
Course Name: Business Law
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course will introduce the student to basic ethical theories and value systems. Students will apply these perspectives to moral issues, problems, and situations which arise within the business environment. Emphasis will be placed on how the applicable laws are being interpreted
Course Name: Canadian Business Law
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course aims to introduce the nature and framework of Canadian law and its implementation and segmentation. Should focus on the study of contract law and tort law. This course provides a foundation for future research on construction contracts and contracts administrative.
Course Name: International Business
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course illustrates how successful managers must function in a competitive world. We will have lots of examples that reflect the vibrancy of the international business field. We will learn managerial approach that keeps an emphasis on skills development, emerging markets, and geographical literacy. We also greatly emphasize cultural literacy and gives students the tools to effectively communicate with foreign business representatives which help students successfully conduct business with organizations worldwide.
Course Name: Business Design
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
Focusing on function management rather than function operation, this course explores in detail the nature of business to-business markets and the differences in industrial buyer behavior and the marketing mix from that encountered in consumer markets.
Course Name: Business Ethics
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course examines specific features of business life through case and case studies, examines ethical dilemmas and issues that arise in business, and considers reasonable ways to apply ethical principles and standards to business. Ethics is also about good and bad, so the course will also address the role of business ethics in human life, while exploring topics such as corporate responsibility and conflicts of interest, employee rights, and advertising and disclosure.
Course Name: Principles of Ethical Leadership
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course explores the ethical framework of moral behavior and moral influence within which truly effective leadership is rooted. This course considers the normative theories of leadership, issues of character, the practice of ethical decision making, general ethical perspectives, leading effectively in times of ethical crisis, and creating an ethical organizational climate.
Course Name: Business Management
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
A study and analysis of the problems of operating a small business. Additionally, a discussion of the how’s, what’s and why’s an individual would consider in developing their own business. All areas of managing an entrepreneurial operation will be covered such as marketing, finance and financial controls, government regulations and strategic planning.
Course Name: Business Strategy
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course includes the study of strategic plans, including the formulation of mission
statements, analysis of external environment and internal organizational factors, the
development of strategic choices, the selection of appropriate choices, the implementation of strategies, and competitive strategies and motivations. Special emphasis was placed on the integration and coordination of internal functional areas enterprise. The case method will be used to provide practical experience in the analysis and decision making of business problems.
Communication
Course Name: Public Speaking
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This skills-based course focuses on the practical skills of public speaking through theory. We will study concepts and models of communication and use visual AIDS to enhance the speaker's performance. Topics include how to tailor your presentation to different situations and audiences, how to effectively support your ideas, how to select and organize materials for your presentation, and how to use multimedia tools in your presentation.
Computer Science
Course Name: Computer Science I
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course is an introduction to fundamental concepts of programming and computer science. This course includes basic programming constructs such as variables, functions, conditions, exceptions, loops, tuples, lists, sets, dictionaries,files, class, objects and methods. It also includes basic algorithmic techniques, object-oriented programming, test-driven development and problem-solving. Previous programming experience is not required.
Course Name: Programming in Java
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course introduces the main purpose of the Java language programming method, new methods based on computer science. In the first part of the course, students will learn programming: software impose hierarchical structure development technology on program design. In the second part of the course, students will learn object-oriented principles programming (OOP): Object-based programming technology. The course includes algorithm construction principles, basic Java commands, control structures, arrays, various methods (including recursive methods), principles of object-oriented programming, collection, dynamic data structure and file operations.
Course Name: Data Structures
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course teaches different techniques of storing, accessing and processing data as utilized in the development of programs and algorithms. Topics include linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, recursion and graphs. Algorithms for applications such as sorting, searching and merging will be analyzed and implemented. Solutions are designed using object-oriented techniques and implemented in the C++ programming language. This course is the third course in the C++ programming sequence and is a required course for students in the Computer Information Systems General Option.
Course Name: Design and Analysis of Algorithms
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course introduces the fundamental elements of the design and analysis of computer algorithms. Focusing on both the underlying mathematical theory and practical considerations of efficiency. Topics include asymptotic notations and analysis, divide and conquer strategy, greedy methods, dynamic programming, basic graph algorithms, NP-completeness, and approximation algorithms. For each topic, beside in-depth coverage, one or more representative problems and their algorithms shall be discussed.
Course Name: Database Management System
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course focuses on the concepts and structures required to design and implement a database management system. Various modern data models, data security and integrity, and concurrency will be discussed. The course will take the form of a group project to design and implement SQL database systems.
ECONOMICS
Course Name: Microeconomics
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course introduces students to the principles of microeconomics. The topics of
the course include supply and demand, elasticity, market efficiency, taxation and
impacts, externalities, public goods and free rider problem, common resources and
the tragedy of the commons, production and costs, competitive firm pricing and
output, monopoly firm pricing and output, monopolistic competitive firm pricing and
output, oligopoly firm pricing and output.
Course Name: Macroeconomics
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course is an introduction to macroeconomics. An analysis of the economy as a
whole including measurement and determination of aggregate demand and
aggregate supply, economic growth, the business cycle, unemployment, inflation, national income, and fiscal policy and monetary policy.
Course Name: Intermediate Microeconomics
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course focuses on the following topics: basic theory of consumer behaviour, production and cost, partial equilibrium analysis of pricing in competitive and monopolistic markets, overall equilibrium welfare, and externalities. More topics will be course if we have enough time. It is recommended for students planning to apply for postgraduate courses in economics, accounting or finance.
Course Name: Intermediate Macroeconomics
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course uses the tools of macroeconomics to deeply study various macroeconomic policy issues. Problems include long-term economic growth, medium-term government finances, and short-term economic stability. Many economic models in use today have been investigated. It is recommended for students planning to apply for postgraduate courses in economics, accounting or finance.
Course Name: Money and Banking
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
It provides students with the opportunity to learn and discuss the topics of money, money markets, money market participants, monetary policies and its effects, and regulation of money markets, in addition to examining banks, banking services, and the banking industry. The dynamic nature of the banking industry will be examined, highlighting recent changes and expected future developments. Students will also learn to identify and manage financial risks.
Course Name: Econometrics
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
Introduction to econometric models and techniques, simultaneous equations, program evaluation, and emphasis on regression. Advanced topics include instrumental variables, panel data methods, measurement errors, and limited dependent variable models.
Course Name: Advanced Microeconomics
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
In this microeconomics course, students will examine the behavior of individual
economic agents and their interactions in diverse market structures by covering four
primary sections: consumer theory, producer theory, market structures and competitive dynamics, and market failures. By exploring concepts such as utility maximization, cost minimization, game theory, and externalities, students will gain a strong foundation in microeconomic principles and analytical methods to effectively address various economic problems.
Engineering
Course Name: Engineering Graphics
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
The course will introduce the students to the Computer-Aided Drafting and Design (including graphic entities, hatch patterns, layering, and information extraction), object visualization, Isometric drawings and Multi-view projection. Two-dimensional drafting and pictorial drawings using a CAD system. Descriptive geometry.
Course Name: Mechanics of Solids
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course is designed to gain insight into the bending and axial deformation behavior of structural elements and structures such as beams, columns, shafts, trusses, frames, etc. Continuing the previous load on the structure - deformation and stress - the process of strain behavior This course is designed to explore the relevant theories and their applications, emphasizing the basic requirements for meeting the balance of forces, deformation compatibility and material behavior conditions. The choice of class assignments and tutorials will highlight the application of theory in a variety of engineering environments.
Course Name: Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course provides an advanced exploration of machine element design and integration, covering components such as bearings, springs, gears, cams, and mechanisms. The instruction is grounded in rigorous application of physics, mathematics, and key mechanical engineering principles, including solid mechanics, fluid mechanics, manufacturing, estimation, and computer simulation. Problem sets aligned with project deliverables enable students to deeply understand the course material. Assessment is based on students' mastery of the course content and their ability to synthesize, model, and fabricate a mechanical device, considering engineering constraints such as cost and schedule.
Course Name: Advanced Engineering Graphics
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
The course is an advanced course which students continue at the Computer-Aided
Drafting and Design Descriptive geometry. We will use AutoCad and Solidworks. You are required to be adept at both software. You will have several projects during the whole semester.
Course Name: Machine Design
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course provides an advanced exploration of machine element design and integration, covering components such as bearings, springs, gears, cams, and mechanisms. The instruction is grounded in rigorous application of physics, mathematics, and key mechanical engineering principles, including solid mechanics, fluid mechanics, manufacturing, estimation, and computer simulation.
Problem sets aligned with project deliverables enable students to deeply understand the course material. Assessment is based on students' mastery of the course content and their ability to synthesize, model, and fabricate a mechanical device, considering engineering constraints such as cost and schedule.
English
Course Name: English Composition I
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course emphasized the fundamentals of written communications, including expository prose, reading comprehension and interpretation, and rhetorical modes.
Individual instructors develop the schedule of instruction and assignments for each course they teach and provide this information on a course syllabus. The outline which follows is confined to topics that commonly appear on course syllabus for English composition I.
Course Name: English Composition II
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
In this course, students will practice college-level critical writing while exploring tools and techniques for teaching and learning. From the printing press to the Amazon Kindle, from Plato’s cademy to massive open online courses (MOOCs), new tools and ideas have found applications in education. Some tools have been evolutionary while others have been so new and different that they “disrupt” the status quo. What external factors make such disruptive changes possible and even successful? Which of the new tools available today will be useful for teaching and learning in the long term, and which will be just fads? The class will consider which innovations are truly helpful to students, which are merely evolutionary and which are truly disruptive. We will also consider the other sense of “disruptive”. Do some tools take learners so far from the subject that they are distracting and disruptive to learning? Students will have an opportunity to research the arguments for and against the use of new tools in education, and will learn about tools that they want to implement or possibly avoid in their own education.
Course Name: Technical and Business Writing
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course will expand upon your effective writing and critical reading abilities. Stresses invention, drafting, revising, editing, and self-assessment, along with effective critiquing and collaborating. You will also learn how to locate academic sources and how to approach these academic sources in a critical way.
Course Name:The Art of Film
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course is designed to help students become more active, critical viewers of films and to be able to communicate that understanding in writing. Like written forms of literature, movies are texts that can be analyzed and interpreted. In the course, students will view a number of films from different time periods, genres, and artistic approaches. Lectures will concentrate on the narrative and stylistic elements used by film makers.
Course Name: British Literature
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course is designed to introduce the British literature chronically from its beginning to around 18th century. Most texts are in English; some are read in translation. The course focuses on connections between literature, power, and the formation of literary canons. We will cover all major genres of early British literature.
Environmental Science
Course Name: Introduction to Environmental Science
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
The environment affects our way of life in many ways. Adverse effects on this environment can affect the well-being of humans and other organisms. Therefore, students must understand natural environmental systems, the physical and social causes of environmental problems, and strategies to mitigate or manage these problems. The course is also designed to help environmental science students determine which majors they would like to pursue within their major.
Japanese
Course Name: Elementary Japanese
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course is designed for students who do not have a basic knowledge of Japanese and gives them the opportunity to develop basic competencies in modern Japanese at an elementary level. We focus on four areas of language ability; Listen, say, read and write. In addition, students will gain a basic knowledge and understanding of Japanese culture. Teachers will introduce and explain new modes of expression and grammar, giving students opportunities to practice and helping them learn to speak and perform correctly in a variety of cultural and social situations. This course covers lessons 1 to 6 of “Genki” textbook
Course Name: Intermediate Japanese
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course is designed for students who had completed Jap 011 and gives them the opportunity to develop fundamental proficiency in modern Japanese at an elementary level. We focus on four aspects of language ability: listening, speaking, reading and writing. This course covers lessons 7 to 12 of “Genki” textbook.
Mathematics
Course Name: Calculus I
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course introduces the differentiation of algebraic and prior functions, application of derivatives, differentiation, indefinite integral, definite integral. Partially meet the core math requirements. The goal here is to develop students' geometric insight into the concepts of difference and integration, and to apply these concepts to problem-solving and "real-world applications."
Course Name: Calculus II
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
Continuation of MATH 011. Topics include integrated technology, applications of definite integration, introduction to incorrect integration, introduction to differential equations, the convergence of sequences and series, Taylor series, parametric equations and poles coordinate
Course Name: Applied Calculus
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
pplied Calculus is an introductory calculus course for students majoring in business, economics, social sciences, and life sciences. In this course, students will learn about two important fundamental topics in calculus: differentiation and integration of functions. Students will learn how to distinguish between different types of functions, including polynomial, rational, exponential, and logarithmic functions, and will learn different integration techniques. Students will also develop an understanding of mathematical modeling, or how to use functions and data to model real-world situations. Throughout the course, students will learn the skills and techniques of calculus, as well as the application of calculus.
Course Number: MATH 031
Course Name: Calculus III
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This is an advanced calculus course for students of greater aptitude and motivation to
learn beyond Calculus II. Topics include: Vectors, lines, planes; Multiple integration;
Cylindrical and spherical coordinates; Functions of several variables: partial derivatives, gradients, chain rule, directional derivative, maxima/minima; Scalar and vector fields, potentials, approximation, multivariate minimization; Lagrange Multipliers; Derivatives of vector valued functions, velocity and acceleration; Stokes's and related theorems; Green's theorem; Prerequisite: MATH 021 or equivalent 2nd year calculus course.
Course Name: Differential Equation
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This is an advanced calculus course for students of greater aptitude and motivation. Topics include: Ordinary differential equations first order; Second-order ordinary differential equations; systems of ordinary differential equations; Laplace transforms; Introduction to higher-order linear differential equations.
Course Name: Mathematical Reasoning
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
The main objective of this course is to bridge the gap between introductory mathematics courses in algebra, linear algebra, and calculus, and advanced mathematics courses such as mathematical analysis and abstract algebra, which usually require students to provide proofs of propositions and theorems. This course is designed to improve the students' understanding of the nature and methods of mathematical proof by means of practice and participation. This course will discuss topics such as logic, naive set theory, basic proof techniques, mathematical induction, functions, relations, cardinality, examples from basic number theory, an introduction to epsilon-delta proofs, combinatorics, etc. and if time allows, we will cover further examples.
Course Name: Foundation of Analysis
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course serves as an introductory course in more rigorous advanced calculus and analysis. It covers real numbers, sequences, series, continuous functions, differentiation, and integration. Students will be able to construct the real number system and to apply abstract mathematical thoughts to mathematical problems after completing this course. This course emphasizes understanding, constructing, and writing proofs.
Course Name: Linear Algebra
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
Linear Algebra is a mathematics area that deals with the study of properties and applications of vectors, matrices and other mathematical structures. Solving systems of linear equations is a basic tool of many mathematical procedures used for solving problems in science and engineering. This course is designed to introduce students to matrix algebra and solutions of linear systems. Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to solve linear equations, use matrix and vector algebra, calculating determinants, finding eigenvalues and eigenvectors, apply basic strategies of mathematical proof and work with applications with linear algebra.
Course Name: Mathematical Theory of Probability
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
•interpret a broad range of word problems related to probability, and determine the
appropriate techniques to apply to solve them
•understand conditional and unconditional probabilities, recognize the difference
between them, and carry out relevant computations
•understand the notion of random variable, and recognize the distinctive properties
of the major discrete and continuous random variables
•apply techniques of single and multivariable calculus, as needed, to compute
probabilities
•compute expected values of random variables, and understand the significance of
expectation as it arises in applications
•recognize the far-reaching role of conditioning in probability questions
•compute moment generating functions of random variables, and use their properties in applications
•understand the statement and significance of the Central Limit Theorem
Course Name: Applied Statistics
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course provides an introduction to fundamental concepts of statistics through examples including design of an observational study, industrial simulation. Theoretical development motivated by sample survey methodology; Randomness, distribution functions, conditional probabilities; Derivation of common discrete distributions; Sampling, regression and correlation analysis, curve fitting, chi-square analysis, test of significance; Expectation operator; Statistics as random variables, point and interval estimation; Maximum likelihood estimators; Properties of estimators. Excel, R, SAS or other statistical software are all acceptable for the data analysis.
Course Name: Statistics and Probability
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This courses provides a practical approach to probability and statistical methods.
Topic includes: Discrete and continuous random variables and probability distribution, Joint probability distributions, Estimation of Parameters and Sampling Distribution,
Statistical Intervals, Tests of Hypotheses, Linear Regression.
Marketing
Course Name: Introduction to Marketing
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course is intended as an overview of marketing. You will learn to respond to consumers' requirements, how the process of creating and providing goods and services. You will study the function of marketing in organizations. Also, analysis of the marketing functions of price, promotion, place, and product will be another core part of this class.
Course Name:Introduction to Consumer Behavior
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
The purpose of this course is to provide you with a practical knowledge of key theories and research findings concerning customer behavior. Explain market behavior by drawing on a variety of social sciences, including psychology, sociology, and anthropology. Students will explore how perception, learning, memory, personality and attitudes influence consumer behavior, how consumption changes over its life cycle, and the powerful influence of culture and subculture on consumers.
Science
Course Name: General Biology
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course will explore biology from the biochemical level through the individual organism. This includes cells, tissues and organ systems; genetics, DNA and protein synthesis, life cycles and development; the internal workings of the cell, and the physiology of organisms from single celled bacteria through multi-cellular plants and animals. Students will investigate the properties of life that unite all living organisms: how they are constructed, reproduce, and function. The course will also highlight the interactions between organisms and their environment in explaining the principles of speciation and biodiversity. Additionally, the course will teach how the processes of scientific investigation can lead to new discoveries.
Course Name: General Biology
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course is a continuous course for the Bio 011. It gives student an overview of the plant form and function, animal form and function, and ecology. A comprehensive lecture laboratory is included in this course to help students better understand. The laboratory section arranged throughout the semester enables students to strengthen the concepts covered in the lecture.
Course Name: Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This is a lecture component of a comprehensive lecture laboratory course that
introduces the concept of the structural / functional relationships between
biological molecules, cell metabolism, and genetics and molecular biology.The
laboratory section arranged throughout the semester enables students to
strengthen the concepts covered in the lecture.
Course Name:Anatomy and Physiology I
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
Anatomy and Physiology I is the first part of both courses. It is the study of the
structure and function of the human body, including cells, tissues and organs of the following systems: skin, bones, muscles, nerves and special senses. The focus is on the interrelationships between the systems and the physiological functions needed to maintain homeostasis.
Course Name: Ecology
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
Ecology covers species, communities, and ecosystem-level ecology of plants and animals. It focuses on interactions between living things and non-living environments. In ecology, almost everything depends on something else. This makes it very difficult to consider facts in isolation. We will consider the relationship between basic ecology and current environmental problems through different concepts and facts.
Course Name: Nutrition
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course introduces the basic facts and principles of human nutrition in terms of the biology and chemistry of nutrients. How they are metabolized and what they do in the body. Emphasis is placed on the study of nutrition, nutrients and their uptake, digestion, absorption, transport, metabolism, interaction, storage and excretion.
Course Name: General Chemistry I
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
The course will introduce the student to the world of chemistry, with emphasis on the
structure of matter. Problem solving, data evaluation, and analysis are stressed.
Applications of chemistry to daily life are include. The lab complements topics in lecture, with lab calculations providing opportunity to use the data the students have gathered.
Course Name: General Chemistry II
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course will continue to study the principle of chemical equilibrium and the
rate and mechanism of chemical reactions. Topics include solutions, chemical
kinetics, chemical equilibrium, chemical thermodynamics, acid& bases,
electrochemistry, thermodynamics and nuclear chemistry. Each week we are
going to have a three hour lab which will reinforce the lecture material.
Course Name: General Physics I
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course provides the introduction to principles and methods of physics.
Topics include Newton's laws; gravitation; mechanics, kinematics; energy
and momentum conservation, rotational motion, and angular momentum
conservation; simple harmonic motion; mechanical waves; fluids; ideal gas
law; heat and the first and second laws of thermodynamics. Atomic and
nuclear physics, and relativity are treated.
Course Name: General Physics II
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
General Physics II is the second part of a one-year course in physics. In this course, students will learn the basics of physics, i.e. electricity and magnetism, such as Coulomb's law, electric field and potential, electric currents and circuits, induction, electromagnetic wave and lights, and introduction to the special theory of relativity and quantum physics. Students are welcome to ask questions before, after and in the middle of the class. Lecture notes will be given on the site, which will be informed later.
Humanities
Course Name: Introduction to Psychology
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
An introductory survey of the scientific studies of human behaviour on the following topics: Human development, physiology, learning, individual differences, motivation, perception, personality, abnormal and social behaviour.
Course Name: Social Psychology
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
A study of group behaviour and the influence of groups on the perception, thinking, and behaviour of the individual. Topics are chosen from the following: Social influences on the development of personality and attitudes; the causes of human aggression; the nature of prejudice why people conform; why people like each other; and the dynamics of groups.
Course Name: Fundamentals of Psychological Research
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course introduces the fundamental research concepts and terminology. Statistics will be an important tool in this course. By taking this course, you will learn how to evaluating the research and scientific claims. Topic will include: Research Process, measurement, statistics, ethics in psychological research, Experimental and Non experimental Design, hypothesis testing, Quasi-experiments, small-N design and etc..
Course Name: Abnormal psychology
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
The purpose of this course is to provide students with an overview of the psychology of anomie. We will explore mental illness in historical, social, and other contexts as much as possible. We're going to look at the pathologic factors of psychological disorders, and their developmental theories; How to diagnose and evaluate diseases, analyze clinical processes and how to treat them.
Course Name: Human Sexuality
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course explores the basic foundations of human sexuality including an overview of physical and psychological aspects. Special emphasis is also placed on the psychosocial aspects of human sexuality and its impact on individuals and society. Some of the topics to be covered are sexual relations, sexual intercourse, sexuality, sexual orientation, kinship, sexual aggression, pornography and prostitution.
Course Name: Cross Cultural Psychology
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course will provide an overview of the impact of cultural effects on human behavior by focusing on similarities and differences from a global perspective utilizing theories of personality. The purpose of this course is to enhance student sensitivity and awareness of diversity aimed at reducing ethnocentric thinking while sharpening critical thinking skills .
Course Name: Forensic and Criminal Psychology
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This class provides an overview of forensic, criminal, and legal psychology including such topics as interrogations, lie detection, forensic identification, profiling, jury selection, eyewitness testimony, and the death penalty
Course Name: Introduction to Philosophy
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
Philosophy is a course that is essential for living in the multi-cultural environment of today. This class challenges and clarifies what one believes, what one's notion(s) of reality are, what and how one comes to know about the world, and, in general, how one views the world at large. This class is an important element in preparing the student to be a careful and reflective critical thinker while being exposed to the greatest western philosophers who have ever lived. The basic understanding of philosophy and its various components are foundational to the notion of what it means to be an “educated” person in the world in which we live.
Course Name: Chinese Religion
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course provides a historical introduction of Chinese religion that explores the diversity and unity of Chinese traditions. Attention is given to the cultural background, art, literature, philosophy, and institutional development of each tradition. Topics covers ancient mythology, cosmology, shamanism; Confucianism and the traditional state cult, Taoist mysticism, and immortality; Buddhism and Chinese religious transformation.
Course Name: Introduction to Sociology
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
Sociology is a scientific study of social life. Sociologists recognize that all human behavior and interaction take place in a unique social and historical context and that the individual level of experience is made up of a person's group members, culture, interpersonal relationships, and major social institutions (including families, education). A system, Media, Economy, and Country. This course will introduce you to key concepts of sociological theory and methods, as well as some basic arguments about social life. Although a one-semester course cannot cover all subjects of sociology, we will cover society. Learn important substantive topics and issues in each sub-sector, some of which include social stratification, gender, family, medical sociology, crime, and bias. Students will receive a sociology concept toolkit for their own life experiences, Includes interactions with friends, family and romantic partners; education and employment experience; and perceptions of social issues and injustices in the US and elsewhere. We will also discuss how sociological research can provide social policies to improve the lives of vulnerable groups and practical information.
Course Name: Adolescent Development in Diverse Families
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course will introduce human development from the pre-adolescent to adulthood in diverse families, particularly from age 10 to 25, with emphasis on cognitive, socioemotional and physical change.
History
Course Name: US History to 1877
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course explores American history through a thematic survey of colonial British North America and the early United States, from the first permanent English settlements of the early seventeenth century to the onset of the American Civil War. It studies how the United States, at first only a series of borderland outposts, became a sprawling national republic for the purpose of investigating factors that brought Americans together and those that tore them apart, as they struggled passionately over racial, religious, and sectional values.
Course Name:US History since 1865
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
Survey of American history from post Reconstruction to the contemporary era, including industrialization, emergence as world power, World War I, Great Depression, World War I, Cold War, the expanding role of government, and global issues in the post Communist era.
Course Name: Introduction to African History
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course explores political, religious, economic, and social development of the peoples of Africa from about 500 AD to the present. Overall this course examines the transformation of Africa from colonial domination to postcolonial states, social movements, and ideologies. Emphasis on social and political relations in African states slavery and the slave trade in West Africa the impact of Christianity and Islam on African colonialism colonialism and its consequences nationalist movements and de colonization pan-Africanism and the politics of African unity.
Course Name: Introduction to Asian American History
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course will introduce and examine major themes in Asian American history. The Asian American community has a long history in the United States starting with immigration to the Americas during the 1960s and has continued to today. We will discuss major themes such as race and class relations, gender and family relations, immigration flows and adaptation patterns, globalization, civil rights/political participation, class and community, and social movements.
Course Name: World History
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course will introduce how the global cultural, social, economic, and political topics take shape and impact each other under the influence of historical and environmental factors. Students will survey the history of how the world developed during the past five centuries and became the globalized world today.
Course Name: 20th and 21st Century World History
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course focuses on world history from the early 20th century to the present. It examines relations among the major powers, the impact of imperialism, the growth of global political economy, and the differing patterns of industrialization, modernization and cultural development throughout the period. In addition to analyzing the origins, course, and consequences of world wars and regional conflicts, students will examine global movements with special reference to gender, class, and cultural issues.
Political Science
Course Name: Introduction to World Politics
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course examines "big questions" in world politics: Why do countries fight wars? Can nuclear proliferation be curtailed? Does trade help developing countries or harm them Topics include rise, development and changes of the nation state system patterns and causes of international conflict and cooperation the environment, redistribution of wealth, security and human rights international law, organizations, and transnational institutions the roles of both state and non state actors in international politics and the methods used to understand this field.
Course Name:Introduction to the U.S. Political System
Credit Hours:4
Course Description:
This course provides an overview of governmental institutions and processes in the United States, the political forces that combine to shape them, and how we might best understand the system that government and politics create. Emphasis on Congress, political parties, pressure groups, growth of the Presidency, the Supreme Court, judicial review, federalism, separation of powers, and the Bill of Rights the executive, administrative agencies, and the judiciary constitutional development and law Relations between formal institutions, parties, and interest groups. Comparisons with other political systems and generalizations are applied to several policy issues.
Please contact via
Wechat:

Email:
249103968@qq.com
Application Form.
Recent Transcript.
Passport Scan Doc.
Personal ID Scan Doc.
Summer Session:
2025/05/05 -2025/08/17
Tel: +86 173-1893-0880
Email: 249103968@qq.com
siexhu@mail.xhu.edu.cn
Wechat:
